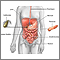
Heartburn is a painful burning feeling just below or behind the breastbone. Most of the time, it comes from the esophagus. The pain often rises in your chest from your stomach. It may also spread to your neck or throat.
Causes
Almost everyone has heartburn at some time. If you have heartburn very often, you may have gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
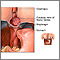
Normally when food or liquid enters your stomach, a band of muscle at the lower end of your esophagus closes off the esophagus. This band is called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). If this band does not close tightly enough, food or stomach acid can back up (reflux) into the esophagus. The stomach contents can irritate the esophagus and cause heartburn and other symptoms.
 Watch this video about:Heartburn
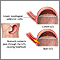
Watch this video about:HeartburnHeartburn is more likely if you have a hiatal hernia. A hiatal hernia is a condition which occurs when the top part of the stomach pokes into the chest cavity. This weakens the LES so that it is easier for acid to back up from the stomach into the esophagus.
Pregnancy and many medicines can bring on heartburn or make it worse.
Medicines that can cause heartburn include:
- Anticholinergics (such as medicines used for sea sickness)
- Beta-blockers for high blood pressure or heart disease
- Bronchodilators for asthma or other lung diseases
- Calcium channel blockers for high blood pressure
- Dopamine-like drugs for Parkinson disease
- Progestin for abnormal menstrual bleeding or birth control
- Sedatives for anxiety or sleep problems (insomnia)
- Theophylline (for asthma or other lung diseases)
- Tricyclic antidepressants
Talk to your health care provider if you think one of your medicines may be causing heartburn. Never change or stop taking medicine without talking to your provider first.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Get urgent medical care if:
- You vomit material that is bloody or looks like coffee grounds.
- Your stools are black (like tar) or maroon.
- You have a burning feeling and a squeezing, crushing, or pressure in your chest. Sometimes people who think they have heartburn are having a heart attack.
Contact your provider if:
- You have heartburn often or it does not go away after a few weeks of self-care.
- You lose weight that you did not want to lose.
- You have trouble swallowing (food feels stuck as it goes down).
- You have a cough or wheezing that does not go away.
- Your symptoms get worse with antacids, H2 blockers, or other treatments.
- You think one of your medicines may be causing heartburn. DO NOT change or stop taking your medicine on your own.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Heartburn is easy to diagnose from your symptoms in most cases. Sometimes, heartburn can be confused with another stomach problem called dyspepsia. If the diagnosis is unclear, you may be sent to a doctor called a gastroenterologist for more testing.
First, your provider will do a physical exam and ask questions about your heartburn, such as:
- When did it begin?
- How long does each episode last?
- Is this the first time you have had heartburn?
- What do you usually eat at each meal? Before you feel heartburn, have you eaten a spicy or fatty meal?
- Do you drink a lot of coffee, other drinks with caffeine, or alcohol? Do you smoke?
- Do you wear clothing that is tight in the chest or belly?
- Do you also have pain in the chest, jaw, arm, or somewhere else?
- What medicines are you taking?
- Have you vomited blood or black material?
- Do you have blood in your stools?
- Do you have black, tarry stools?
- Are there other symptoms with your heartburn?
Your provider may suggest one or more of the following tests:
- Esophageal motility to measure the pressure of your LES
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD or upper endoscopy) to look at the inside lining of your esophagus and stomach
- Upper GI series (most often done for swallowing problems)
If your symptoms do not get better with home care, you may need to take medicine to reduce acid that is stronger than over-the-counter medicines. Any sign of bleeding will need more testing and treatment.
Alternative Names
Pyrosis; GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease); Esophagitis
Patient Instructions
References
DeVault KR. Symptoms of esophageal disease. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 13.
Mayer EA. Functional gastrointestinal disorders: irritable bowel syndrome, dyspepsia, chest pain of presumed esophageal origin, and heartburn. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 128.
Review Date 1/30/2023
Updated by: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.