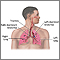
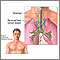
Mediastinitis is swelling and irritation (inflammation) of the chest area between the lungs (mediastinum). This area contains the heart, large blood vessels, windpipe (trachea), food tube (esophagus), thymus gland, lymph nodes, and connective tissue.
Causes
Mediastinitis usually results from an infection. It may occur suddenly (acute), or it may develop slowly and get worse over time (chronic). It most often occurs in people who recently had an upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy or chest surgery.
A person may have a tear in their esophagus that causes mediastinitis. Causes of the tear include:
Other causes of mediastinitis include:
- A fungal infection called histoplasmosis
- Radiation to the chest
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, or other tissues (sarcoidosis)
- Tuberculosis
- Breathing in anthrax
- Cancer
Risk factors include:
- Disease of the esophagus
- Diabetes mellitus
- Problems in the upper gastrointestinal tract
- Recent chest surgery or upper GI endoscopy
- Weakened immune system
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms and medical history.
Tests may include:
Your provider may insert a needle into the area of inflammation. This is to obtain a sample to send for a Gram stain, other stains and culture to determine the type of infection, if present.
Treatment
You may receive antibiotics if you have an infection.
You may need surgery to remove the area of inflammation if the blood vessels, windpipe, or esophagus is blocked.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well a person does depends on the cause and severity of the mediastinitis.
Mediastinitis after chest surgery is very serious. There is a risk of dying from this condition.
Possible Complications
Complications include the following:
- Spread of the infection to the bloodstream, blood vessels, bones, heart, or lungs
- Scarring
Scarring can be severe, especially when it is caused by chronic mediastinitis. Scarring can interfere with heart or lung function.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have had open chest surgery and develop:
- Chest pain
- Chills
- Drainage from the wound
- Fever
- Shortness of breath
If you have a lung infection or sarcoidosis and develop any of these symptoms, contact your provider right away.
Prevention
To lessen the risk of developing mediastinitis related to chest surgery, surgical wounds should be kept clean and dry after surgery.
Treating tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, or other conditions associated with mediastinitis may prevent this complication.
Alternative Names
Chest infection
References
Lentz RJ, Loyd JE. Mediastinitis and fibrosing mediastinitis. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 116.
Van Schooneveld TC, Rupp ME. Mediastinitis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 85.
Review Date 8/29/2024
Updated by: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.