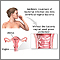
A secondary infection is an infection that occurs during or after treatment for another infection. It may be caused by the first treatment or by changes in the body or immune system that allow a second infection.
Two examples of a secondary infection are:
- A vaginal yeast infection after taking antibiotics to treat an infection caused by bacteria
- Pneumonia caused by bacteria or fungi after having an upper respiratory infection (like a cold) that was caused by a virus
Review Date 8/26/2023
Updated by: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.