



Table of Contents: 2018 JANUARY–FEBRUARY No. 420
Collins M. New Maximum Length for Custom Filters in PubMed. 2018 Jan-Feb;(420):e4.
In April 2018, NLM will start limiting the length of PubMed custom filters to 4,000 characters, and asterisks (*) for truncation will no longer be allowed in these filters. We are introducing a limitation on this My NCBI feature to address resource-intensive demands on the system and to continue providing a rapid response time for all PubMed users.
Custom filters appear on the right sidebar menu and are configured in My NCBI (see Figure 1).
If you use custom filters in PubMed that contain more than 4,000 characters and/or an asterisk (*) for truncation, you can prepare for this change now by updating your custom filters. For any searches that are affected by this change, click on the gear icon (see Figure 2) and edit the search so that it contains fewer than 4,000 characters and no asterisks.

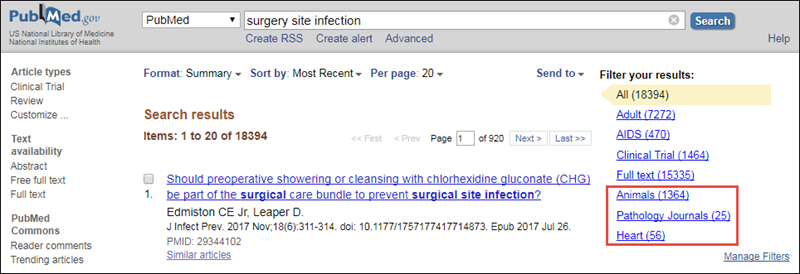
After the new rules are implemented, custom filters that exceed 4,000 characters and/or include an asterisk (*) will be disabled. In this example, the filter named "Heart" contains more than 4,000 characters and/or an asterisk (*) for truncation. Under the new rules for custom filters, the filter "Heart" is deselected on this page and no longer appears on the results page in PubMed. Custom filters that do not exceed 4,000 characters or include any asterisks (*) are not affected. In the example above, the custom filters "Animals" and "Pathology Journals are not affected and remain active on the results page in PubMed. Standard filters are not affected.
You can also create a saved search with the entire search from the affected filter (see Figure 3).

 Figure 4: Configure your saved search.
Figure 4: Configure your saved search.To use this saved search in place of a filter:


By
Marie Collins
National Center for Biotechnology Information